► Kênh hỏi đáp và giải thích thắc mắc kiến thức MIỄN PHÍ → truy cập LINK NHÓM: ENGLISH AMOM
► Kênh YOUTUBE hệ thống toàn bộ bài giảng CLIPS: truy cập LINK: ENGLISH AMOM CHANNEL
► Kênh TIKTOK: ENGLISH AMOM
READING
1) Read the text about the causes and effects of counter-urbanisation.
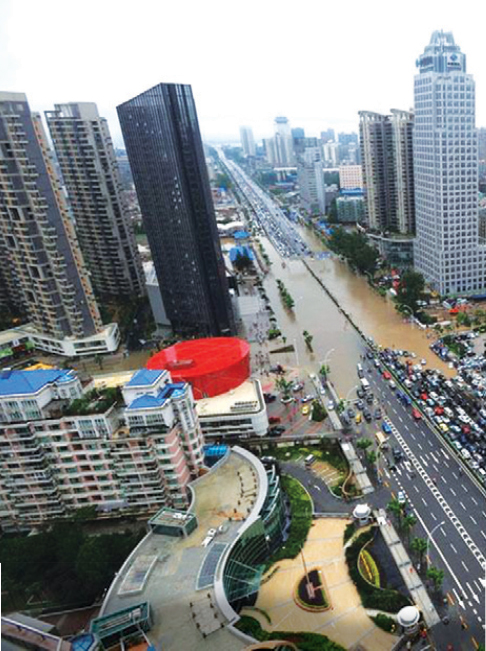

Counter-urbanisation
While urbanisation has led to fast urban growth, counter-urbanisation has resulted in the opposite situation. Counter-urbanisation happens when a great number of people move from urban areas into rural areas.
This phenomenon is linked to the ‘push’ and ‘pull’ factors of migration. Trying to avoid overcrowded inner cities, city dwellers look for larger, cleaner and quieter houses with more land at cheaper prices in rural or suburban areas. They want to escape the air and noise pollution, and the crime in inner cities.
However, counter-urbanisation causes serious problems in the shrinking cities. These cities face severe economic strain and a sharp increase in poverty. Despite declining populations, they still have to spend money maintaining infrastructure, such as roads, sanitation, public transport, etc.., built for a much larger population.
Meanwhile, villages in the countryside become increasingly urbanised, grow fast and soon lose their uniqueness and charm. Local prices go up because city migrants have more money. They earn money from well-paid city jobs and high-valued city properties. Villagers often find it more and more difficult to earn a living and provide for their families.
Counter-urbanisation has caused many negative effects. Governments should find urgent short-term solutions before implementing a long-term comprehensive programme to make life sustainable for people in both urban and rural areas.
2) Read the text again and decide whether the following statements are true (T), false (F), or not given (NG), and tick the correct box.
| T | F | NG | |
| 1) Urbanisation and counter-urbanisation are two opposite trends. | |||
| 2) City dwellers look for houses in rural or suburban areas just because they are cheap. | |||
| 3) Shrinking cities still face high rates of crime. | |||
| 4) When populations decline, cities spend less money on maintaining infrastructure. | |||
| 5) Country villages quickly lose their unique character and charm when they become urbanised and grow fast. | |||
| 6) Governments should offer immediate short-term solutions to make life sustainable for both urban and rural inhabitants. |
ĐÁP ÁN:
| 1 – T | 2 – F | 3 – NG | 4 – F | 5 – T | 6 – F |
LISTENING
4) Listen to the recording about wave energy. Choose the best option to complete the sentence.
1. Wave energy, produced by ocean surface waves, is both ..............................
A. friendly and efficient
B. eco-friendly and efficient
C. eco-friendly and cost-efficient
2. Using 1% of wave energy can provide the equivalent of .............................. the energy consumption worldwide.
A. 50 times
B. 500 times
C. 5000 times
3. Building and operating wave power stations in the ocean is far .............................. than on land.
A. more expensive
B. more difficult
C. more expensive and difficult
4. Salt water is a very hostile environment to devices, which become .............................. and cannot last long.
A. rusty easily
B. rusty slowly
C. rusty
5. Progress in renewable energy technology will soon allow Viet Nam to ............................. effectively and effciently.
A. export wave energy
B. exploit wave energy
C. explore wave energy
ĐÁP ÁN:
| 1. C | 2. B | 3. C | 4. A | 5. B |
WRITING
5) Write meaningful sentences about the pros and cons of solar energy. Use the words given.
1. solar energy/ come directly/ sun/ renewable energy source/ sustainable/.
→ .......................................................................................................................................
2. this type/ energy/ environmentally friendly/ not cause pollution/.
→ ........................................................................................................................................
3. solar energy/ available everywhere/ very quiet/ devices/ not have moving parts/.
→ .......................................................................................................................................
4. solar panels/ expensive/ use rare/ special materials/ technology/ store solar energy/ costly/.
→ .......................................................................................................................................
5. solar energy/ not always available/ access/ sunlight/ limited/ certain times/.
→ .......................................................................................................................................
6. although/ greener/ fossil fuels/ production/ solar panels/ emit/ greenhouse gases/.
→ .......................................................................................................................................
ĐÁP ÁN:
1. Solar energy comes directly from the sun and this renewable energy source is sustainable.
2. This type of energy is environmentally friendly and does not cause pollution.
3. Solar energy is available everywhere and is very quiet because solar energy/its devices do not have any moving parts.
4. Solar panels are expensive as they use rare and special materials, and the technology used to store solar energy is costly.
5. Solar energy is not always available since access to sunlight is limited at certain times.
6. Although it is greener than fossil fuels, the production of solar panels may emit some greenhouse gases.